It is well known that any complex sound can be described by three physical quantities of sound: amplitude, frequency and phase. But for the human ear, the sound is described by three other quantities, namely loudness, tone and tone. This is what we usually call "the three elements of sound." In addition, the human ear can distinguish the direction of the sound and the distance to the human ear. The sound engineer can make good sounds if he makes good use of these basic characteristics of the human ear.
The loudness of the loudness sound is related to the amplitude (sound pressure) of the sound wave. For a signal of the same frequency, the louder the sound pressure, the louder the loudness. However, the loudness (sensitivity) of the human ear to sounds of different frequencies is different, that is, different sounds are perceived for sounds of different frequencies and sound pressures. Sounds in the frequency range of 3 to 4 kHz are easily perceived (higher sensitivity), while sounds in the lower or higher frequency range are less susceptible to being perceived. The relationship between the sound pressure level and the frequency under the condition of equal loudness is called the equal loudness curve.
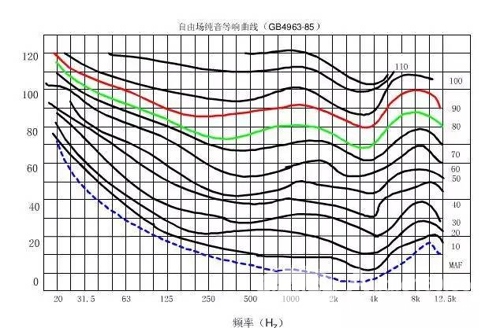
â–³ normal human ear's equal response curve
From the figure we can draw the following simple conclusions:
1 The sensitivity of the human ear to different frequency sounds is different. Specifically, the sensitivity to 3 to 4 kHz sound is higher, and as the frequency increases and decreases toward 3 to 4 kHz, the overall trend is a decrease in sensitivity.
The sensitivity of the 2 human ear to different frequency sounds is also related to the magnitude of the sound pressure. As the sound pressure decreases, the sensitivity of the human ear to low frequency and high frequency is reduced, especially for low frequency sound. That's why when we turn the volume down (ie at low sound pressure levels), even if there are more bass components in the program, it still sounds too low, once the volume is turned on (sound pressure level) At about 80 decibels or more, you will feel the richer bass.
It can be seen from the equal-tone curve that if the sound is reproduced at a lower sound pressure level than the original sound (during recording), it is necessary to pass the equalizer to raise the bass and treble to ensure the original sound balance. For example, a band plays, if both low-frequency and high-frequency sounds are recorded at about 100 decibels, because the equal loudness curve is almost straight, so the bass and treble sound almost the same. If the sound pressure level during playback is low, for example, 50 decibels, then the sound of 50 Hz can be heard just now, while the sound of 1 kHz sounds 50 squares, and the sounds of other frequencies have different loudness. Level, so it sounds like the low frequency sound and high frequency sound are lost, that is, the original sound has changed. At this time, if the sound of 50 Hz sounds roughly the same as the sound of 1 kHz, it must be raised by about 20 decibels. It can be seen that the equal loudness curve is one of the important basis for us to use the equalizer.
Tone pitch, also known as pitch, is the subjective evaluation scale of the human ear to the tone of the tone. The pitch is mainly determined by the frequency. The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch, the lower the frequency, and the lower the pitch. But the pitch and amplitude also have a certain relationship.
The human ear's perception of pitch changes is not a linear relationship, but a logarithmic relationship. That is to say, the pitch feeling is formed by the relative change of the frequency, that is, regardless of the original frequency, the frequency change of the same multiple always produces the same pitch change feeling to the human ear. For example, to double the frequency, for example, from 100 Hz to 200 Hz or from 1 kHz to 2 kHz, the pitch change is the same in the auditory sense, that is, the so-called "octave" is also improved. It is "octave". It is precisely because the pitch change is proportional to the logarithm (or multiple) of the relative change in frequency. Therefore, in the graph showing the frequency, the frequency coordinate is often on the logarithmic scale, and the center in the graphic equalizer is often pressed by 1/2. The same is true for the reason of the "" or "1/3" setting.
The perception of the human ear to the tone is also affected by the amplitude. When the amplitude is large, the eardrum is greatly stimulated and deformed, thereby affecting the nerve's perception of the tone. Generally speaking, when the loudness is increased, the human ear feels that the pitch is lowered, and the lower the frequency, the more the feeling is lowered.
In addition to the obvious ability to distinguish between loudness and pitch, the timbre of the timbre can accurately determine the tone of the sound. The frequency of different instruments is very different. For example, even if the violin and piano play the same high-pitched notes, people can quickly distinguish which is the piano sound and which is the violin sound, and not confused with each other. This is because they have the same pitch when playing the same note, but their harmonic components (overtones) are very different in quantity, frequency and intensity. It is because of the different composition of these harmonics that the unique tone of each instrument is given. The tone is primarily related to the frequency structure of the sound. In fact, most of the vibration of the instrument is not a simple harmonic vibration, but a superposition of many different simple vibrations, and the vibrational frequencies of these simple harmonic vibrations satisfy the integral multiple relationship. Among them, the lowest frequency is called the fundamental frequency, the simple harmonic of the fundamental frequency pair is called the fundamental wave, and the simple harmonic whose frequency is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency is called harmonic, which is called overtone in the music vocabulary. It is precisely because of the different composition ratios of harmonics that it is unique to various instruments and vocals. If there is no harmonic component, the simple pitch harmonic signal is not musical.
When listening to the direction, people can use the ear to determine the direction of the sound and determine the location of the sound source. This is because we have two ears (the so-called "binaural effect"), and the distance between the ears is about 20 cm. When the sound from the same source reaches both ears, there are differences in time, intensity and phase. It is from this difference that we have completed the positioning of “sound imageâ€.
The human ear grows on both sides of the head, and the azimuth resolution ability for the horizontal direction is much stronger than that of the vertical direction. Generally, the horizontal direction of 5°~15° can be distinguished, but in the vertical direction, Sometimes it is more than 60° to distinguish it.
The sense of sense of direction in the sense of hearing makes it possible for us to "concentrate" in a noisy environment to hear a relatively special sound from a certain direction. If we plug one ear and listen to it with a single ear, the above The sense of direction will disappear, and the sound is seriously disturbed by the environment, and the sound is confusing. The use of the sense of sense of direction of the sense of hearing requires us to arrange the speakers in the hall as much as possible to ensure that the direction of "visual" and "listening" is the same, that is, the sound source and the sound seen by the eyes. The source comes from the same direction. This requires us to use a "centralized" sound reinforcement system - focus the speakers on both sides of the stage, and make the speakers as close as possible to the sound source in the horizontal direction, often with less impact.
In addition, the human ear can distinguish the distance of the sound source according to the difference of sound quality, that is, the human ear not only has the ability of "orientation" but also the ability of "positioning".
The effect of noise on clarity
The noise encountered in KTV mainly has two types of electrical noise and environmental noise. Among them, electrical noise can be divided into thermal noise, AC noise, induced noise and the noise floor of the recording medium. However, in recent years, with the rapid development of electronic technology, the emergence of new digital recording methods and a large number of imported equipment with excellent performance, the thermal noise in electrical noise and the noise floor of recording media have become less obvious, so electrical noise Mainly due to AC noise and induced noise caused by poor shielding or grounding in the wiring, these can be suppressed by improving the wiring process or using noise gates. So here Xiaobian focuses on the impact of environmental noise on clarity.
The presence of noise causes a decrease in the hearing of the target sound, that is, a so-called "masking phenomenon" which depends not only on the sound pressure of the noise but also on its frequency components and spectral distribution. Simply put, there are mainly the following characteristics:
1 low frequency sound, especially when the loudness is quite large, it will have a more obvious masking effect on high frequency sound.
2 high frequency sound produces only a small masking effect on low frequency sound.
3 The closer the masking sound is to the frequency of the masked sound, the greater the masking effect. When their frequencies are the same, the masking effect of one sound on the other sound is maximized.
It can be seen that low frequency noise (such as fan noise) and vocals are the main sources of interference. In general, KTV requires an ambient noise level of less than 30 to 35 decibels, which is an important requirement for clarity.
According to the classification of the shape, Telephone Cable have round telephone cable and Flat Telephone Cable.
The common specification of round telephone cable has two core and four core, the wire diameter has 0.4 and 0.5 respectively, some areas have 0.8 and 1.0.In addition to the two and four cores, there are four, six, eight, and ten cores.
If the general family is the local telephone use mode, 2 chip is enough to use.If the telephone is used by a company or part of a group, it is recommended to use a 4-cell line in consideration of the need for telephone broadband, and a 6-cell line is recommended if a digital telephone is used.
Round Telephone Cable,Communication Cable,Telephone Line,Power Wire
Shenzhen Kingwire Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.kingwires.com