A power amplifier (English name: power amplifier), referred to as "power amplifier", refers to an amplifier that produces a maximum power output to drive a load (such as a speaker) at a given distortion rate. The power amplifier plays a pivotal role of “organization and coordination†in the entire sound system, and to some extent dominates whether the entire system can provide good sound quality output.

A power amplifier usually consists of three parts: a preamplifier, a driver amplifier, and a power amplifier (Figure 3).

1. The preamplifier plays a matching role, and its input impedance is high (not less than 10kΩ). It can absorb most of the previous signal, and the output impedance is low (below tens of Ω), which can transmit most of the signal. At the same time, it is itself a current amplifier that converts the input voltage signal into a current signal and gives appropriate amplification.
2. The driver amplifier acts as a bridge, which further amplifies the current signal sent by the preamplifier and amplifies it into a medium power signal to drive the final stage power amplifier to work normally. If there is no driver amplifier, the final stage power amplifier cannot deliver a high-powered sound signal.
3. The final stage power amplifier plays a key role. It will drive the current signal from the amplifier to form a high-power signal, which will drive the speaker to sound. Its technical specifications determine the technical specifications of the entire power amplifier.
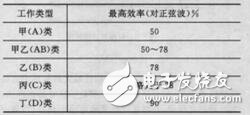
The active components used in the power amplifier in the power amplifier:The active devices used in power amplifiers are mainly transistors (bipolar or field effect transistors). In applications where the operating frequency is high or the output power is high, electron tubes (including high-power transmitting tubes) are also used; traveling waves are used in the microwave section. tube. Power amplifiers can be classified into Class A (A), Class A (AB), Class B (B), Class C (C) and D (D) according to the working point of their active devices. The table lists the highest efficiencies that a power amplifier can achieve for a sine wave with different types of work.
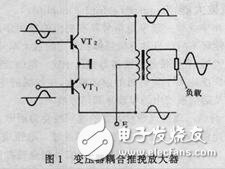
Power amplifiers are often used in broadcast, communication transmitter output stages, audio system output stages, and amplifiers that control system drive actuators. The application requirements are different, the performance requirements are different, and the circuit configuration and work type are also different. Commonly used are linear power amplifiers, resonant power amplifiers, broadband power amplifier circuits. In order to increase the output power, power synthesis technology can be employed. Linear power amplifiers are used where small nonlinear distortion is required. Common circuit forms are single-tube amplifier circuits and push-pull amplifier circuits. The circuit form of the single-tube amplifying circuit is similar to that of the voltage amplifier, and must be Class A operation, which is the least efficient and is mostly used for small power amplifiers. The push-pull amplifier circuit consists of two active devices, each excited with an input signal with a phase difference of 180°, and then their output signals are inverted and supplied to the load.
Figure 1 shows the principle circuit of a push-pull amplifier that uses a transformer to achieve inverse superposition. This circuit theoretically works with two devices operating in class B without distortion. However, the actual active device characteristics are not completely ideal and need to work in Class A and Class B. The push-pull amplifying circuit can also be composed of a transistor of opposite polarity complementary to a CPNP type and an NPN type bipolar transistor pair or an N-channel and P-channel FET pair). Circuits constructed using their complementary characteristics do not require two input signals with phase differences of 180°, and the output signals do not need to be inverted. This circuit can be composed entirely of transistors and resistors, which is easy to integrate and is used for successful integration.
The resonant power amplifier uses a resonant tank as a load for the active device, and an amplifier that specifically amplifies the narrowband signal. This type of amplifier allows the current waveform to be very distorted, and then uses the resonant loop to filter out the harmonics; it allows the active device to operate in Class C for high efficiency; and more for the final stage in high-power transmitters. If the resonant tank is tuned to the harmonics of the input signal and a suitable operating point is selected, a frequency multiplier can be constructed. Broadband power amplifiers use a transmission line transformer as the load for active devices. The upper limit of this power amplifier can reach several hundred megahertz and the band coverage is wide. The transmission line transformer is constructed according to the working principle of the transmission line and the transformer.
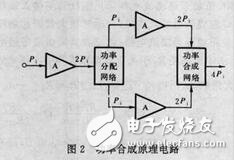
Power Synthesis Technique Multiple amplifiers amplify the same input signal and then combine the output power of each amplifier in a synthetic manner. Figure 2 is a power synthesis principle circuit consisting of an amplifier, a power synthesis and distribution network. Synthetic and distribution networks are commonly used in transmission line transformers. The characteristic of this kind of synthesis technology is that the working state of one of the amplifiers changes, and the work of the remaining amplifiers is not affected. In order to further improve the efficiency of the power amplifier, the input signal is first converted into a pulse sequence, which is amplified and then converted into an analog signal. This kind of power amplifier works in pulse amplification, and the theoretical efficiency can reach 100%, which is called D (D) type amplifier. Since the switching characteristics of active devices are not ideal, increasing the operating frequency of such amplifiers is limited. In the power amplifier, due to the large heat loss, the main heating part of the active device should be added with a heat sink, and sometimes air-cooled, water-cooled or evaporative cooling is used to reduce the temperature rise of the device.
Audio Line Transformer,10W 6Ohm Audio Line Transformer,Audio Line Transformer 100V,Audio transformer for amplifier
Guang Er Zhong(Zhaoqing)Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.poweradapter.com.cn